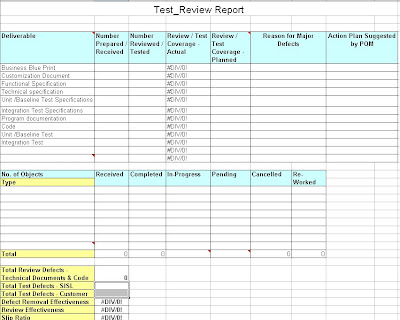
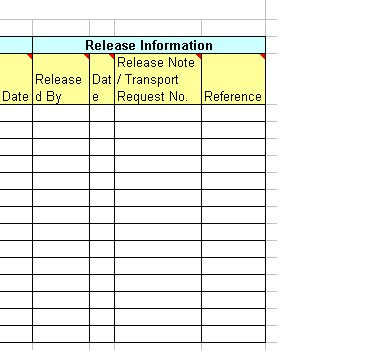
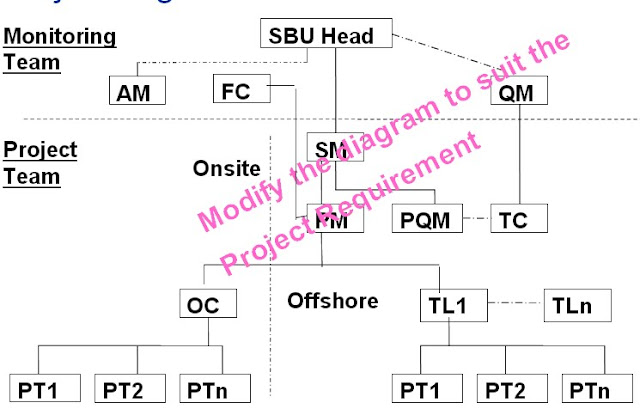
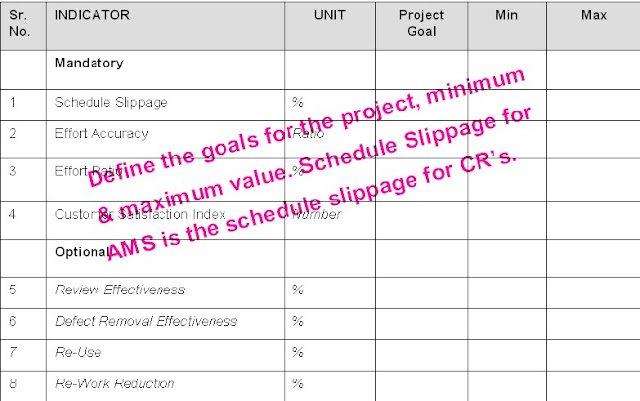
Transportation request: It is a 12 digit alphanumeric number
SE01 to transport the request for business user
SE10 to transport the request to the server
Click on create button
© Select customizing request
Give the short description
Save it
Select/Place the cursor on the request number
Then click on add user icon
Specify your user name and press ENTER
Click on release directly
Basis people maintain connections between Development server and Quality Assurance server. In weekend all the
requests are send to the production server.
NOTE: Once the customization has been transported to the server that cannot be changed.
SE01 to transport the request for business user
SE10 to transport the request to the server
Click on create button
© Select customizing request
Give the short description
Save it
Select/Place the cursor on the request number
Then click on add user icon
Specify your user name and press ENTER
Click on release directly
Basis people maintain connections between Development server and Quality Assurance server. In weekend all the
requests are send to the production server.
NOTE: Once the customization has been transported to the server that cannot be changed.