![]() x Define Condition Types
x Define Condition Types
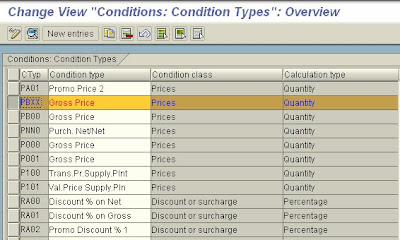
In this step you define condition types.
The condition types are used to represent pricing elements such as prices, discounts, surcharges, taxes, or delivery costs in the SAP System. These are stored in the system in condition records.
You also have the option of entering conditions requiring subsequent (end-of-period rebate) settlement.
A separate topic "Subsequent Settlement" in the Purchasing IMG covers this functionality.
For condition types for which you wish to maintain conditions with their own validity period, you must specify an access sequence. In this way, you stipulate the fields the SAP System is to check in its search for a valid condition record.
Example:
An access sequence has been assigned to condition type PB00 so that prices can be maintained in purchasing info records and contracts.
No access sequence has been assigned to condition type RC00 because it does not have a validity period of its own. In the standard system, it is always maintained simultaneously with the price and is valid for the period of the price.
Note
In a price calculation schema (which may also be termed a "pricing procedure"), you collect together all the condition types that are automatically to be taken into account by the SAP System in the process of price determination with regard to a business transaction.
Note that you can only also enter manually the condition types that are contained in the calculation schema. You can alter the result of the price determination process in the purchasing document manually. You can
limit the change options for a condition type in this step.
SAP recommendation
If you define your own condition types, the key should begin with the letter Z, as SAP keeps these name slots free in the standard system.
You should not change the condition types that are included in the standard SAP System supplied.
Actions
1. Check the extent to which you can use the condition types that are included in the standard SAP
system supplied.
2. Create new access sequences by copying and changing similar existing ones. In doing so, you must specify the following:
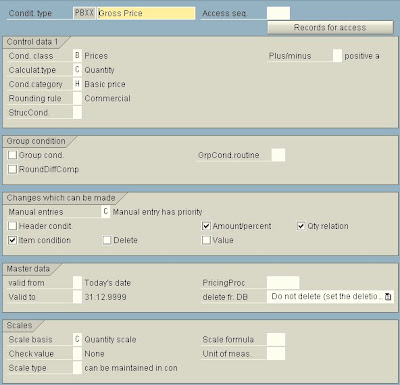
o enter an alphanumeric key (which can have a maximum of 4 characters) for the condition type, together with a descriptive text.
o Specify an access sequence for the condition types. (For header conditions, you need not specify an access sequence.)
3. Maintain the detail screen for the condition type.
Note:
![]() To improve performance, you can optimize the accesses for a condition type. In searching for condition records, the SAP System will then initially check the header fields in the document only.
To improve performance, you can optimize the accesses for a condition type. In searching for condition records, the SAP System will then initially check the header fields in the document only.
![]() x Define Limits
x Define Limits
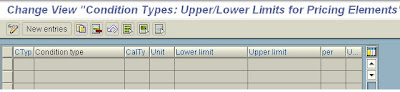
In this step, you can define upper and lower limits for the value of a condition.
In this way, you restrict the amounts or scale values in the relevant contition records. The limits are defined at the level of the condition type.
Actions
![]()
 Maintain the desired limits.
Maintain the desired limits.
![]() x Define Exclusion Indicators
x Define Exclusion Indicators
In this step, you can set exclusion indicators for condition types.
The exclusion indicator prevents the use of too many condition types in the price determination process.
In the standard system, it determines that either the automatic or the manual price is applied, but not both.
Note:
To be able to use the exclusion indicator, you must first maintain a requirement in the step Define
 Calculation Schema.
Calculation Schema.